Government seeks stakeholder input on draft rules by February 18, 2025.
The Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) unveiled the draft Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025 on January 3, outlining robust measures to safeguard personal data, particularly of children. The proposed rules, stemming from the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, seek to bolster accountability and transparency in data handling practices across sectors. Stakeholders have been invited to submit objections and suggestions by February 18, 2025.
Child-Centric Data Protections
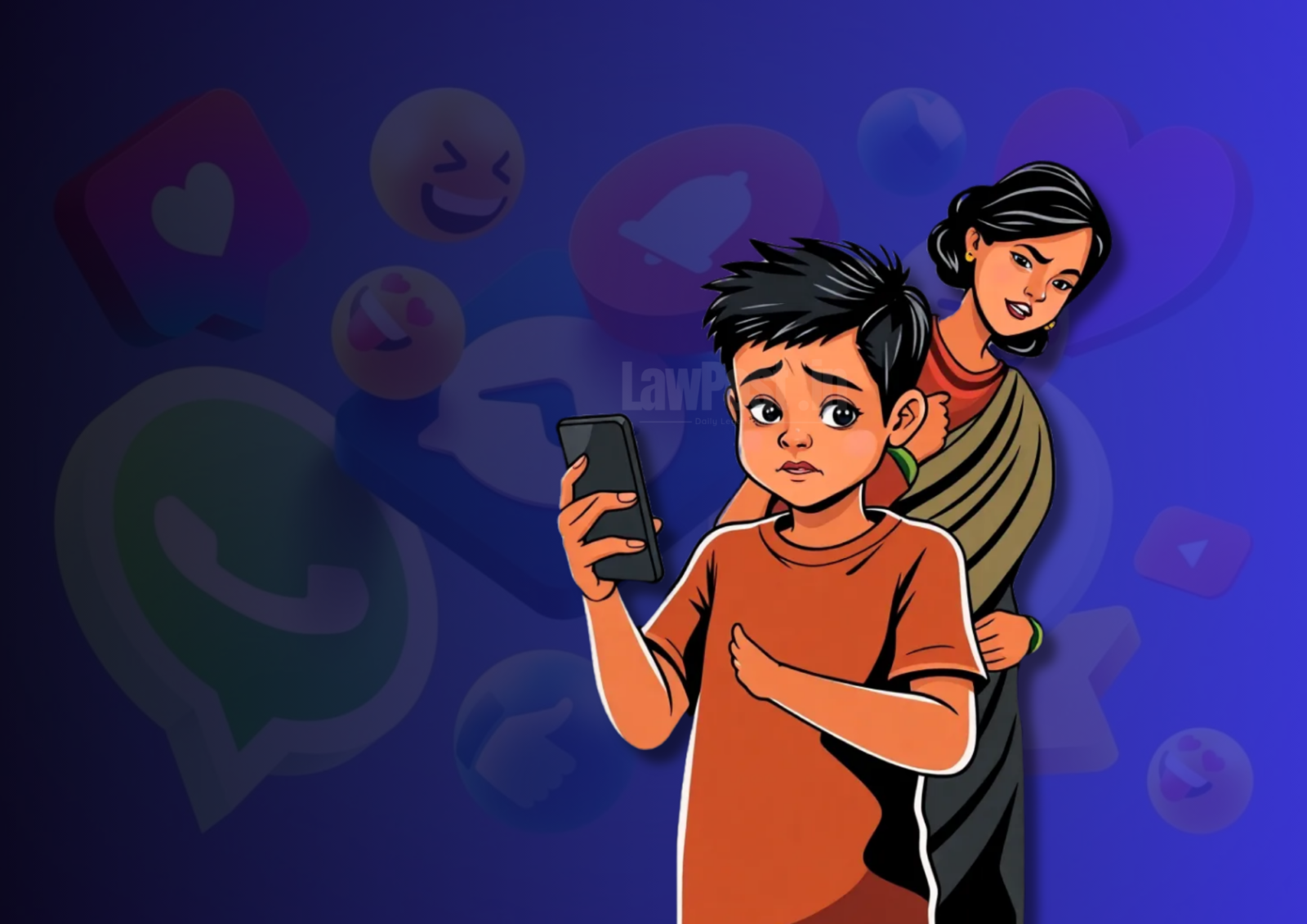
A key focus of the draft rules is the protection of children’s personal data. Social media platforms and online services will now require verifiable parental consent before processing any personal data of minors. The rules mandate that data fiduciaries (entities that handle personal data) must verify the identity of guardians claiming to represent children.
An illustrative case in the draft highlights how these measures would work in practice:
“C is a child, P is her parent, and DF is a Data Fiduciary. A user account of C is sought to be created on the online platform of DF, by processing the personal data of C. DF shall enable C’s parent to identify herself through its website, app, or other appropriate means. Before processing C’s personal data, DF shall confirm that it holds reliable identity and age details of P.”
This framework aims to enhance the accountability of platforms while ensuring parents are actively involved in decisions about their children’s data.
Enhanced Breach Notification Requirements
To tackle the rising incidents of data breaches, the draft rules emphasize timely and transparent reporting. If a breach occurs, data fiduciaries are required to:
- Notify affected individuals with details on the breach’s nature, extent, and potential consequences.
- Inform the regulatory board within a specified timeframe.
These steps aim to ensure quick mitigation of risks and promote trust in digital ecosystems.
Data Retention and Security
The draft proposes stringent data retention policies, requiring fiduciaries to erase personal data that is no longer necessary for its intended purpose. This move is designed to prevent the indefinite storage of sensitive information.
Organisations will also need to implement robust security measures, such as:
- Encrypting and securing personal data.
- Monitoring access to detect unauthorized use.
- Controlling access to computer systems used for data processing.
Processing of Data by State Entities
The rules grant State entities the ability to process personal data when delivering subsidies, benefits, or services, provided such processing adheres to prescribed safeguards. This provision underscores the need for public sector accountability in data handling.
Public Feedback Invited
The government is keen on receiving input from stakeholders to refine these rules. The Ministry stated:
“This framework reflects India’s commitment to safeguarding individual privacy while fostering trust in the digital ecosystem. Stakeholders’ insights are invaluable in shaping a balanced and effective data protection regime.”
Looking Ahead
The Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025, mark a significant step in addressing contemporary privacy concerns, especially for vulnerable groups like children. By introducing stringent regulations and empowering individuals with greater control over their data, the government aims to establish a robust foundation for data privacy in the digital age.
Stakeholders can submit their feedback by February 18, ensuring their voices are part of this transformative journey.